What is a Cell?
- The cell is the basic biological unit of life
- Cells come in many shapes and sizes, but all cells have the same basic parts: a nucleus, cytoskeleton, membrane, and cytoplasm. The nucleus controls the cell’s genetic information and is where DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is stored. The cytoskeleton helps cells move around and divide. The membrane separates the inside of a cell from the outside world. The cytoplasm contains the cell’s metabolic activities. Cells communicate with each other through chemical signals that travel through the cytoplasm.
- Cells are made up of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and other molecules. Proteins are the smallest units of a cell and are responsible for most of the cell’s activity. Carbohydrates provide energy for cells and lipids help cells to resist damage from oxygen and other chemicals. In the human body, cells are organized into tissues and organs. Tissues are groups of related cells that perform specific functions (e.g., muscles or blood). Organs are groups of tissues that perform a single function (e.g., heart or brain).
How Cells Work
- Cells can carry out all the essential life processes, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
- Cells are made up of smaller molecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- The proteins within cells perform many essential functions, including providing structure, catalyzing biochemical reactions, and transporting other molecules across the cell membrane.
Cellular Respiration
The process of cellular respiration is the main way that cells obtain energy from their environment. As its name suggests, cellular respiration is the process by which a cell obtains energy from its environment. The word “respiration” comes from the Latin res (thing) and spirare (to breathe). Cellular respiration is also known as aerobic respiration because it occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Parts of an Animal Cell

Parts of a Plant Cell
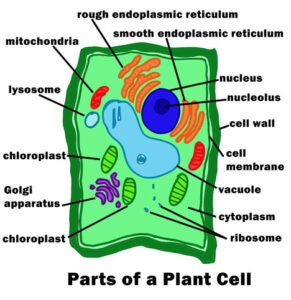
Parts of a Cell
- The cell wall is the outer membrane of a cell. It is made of peptidoglycan, a polysaccharide. The peptidoglycan chains are linked together by cross-links that are formed from lysine and arginine residues.
- The cell membrane is the outermost layer of a cell and is composed of phospholipids. Membrane proteins such as ion pumps, transporters, and receptors are embedded in the membrane.
- The Centrioles are small, rod-shaped structures that are found in all eukaryotic cells. They help maintain the spindle during cell division, and they also help to organize the chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.
- The Chloroplasts, which are the site of photosynthesis in green plants, are bounded by a thick membrane called the thylakoid membrane.
- The Cytoplasm is the internal liquid of the cell and contains all of the organelles, called organelles. The cytoplasm also contains many of the chemical reactions that occur in cells.
- DNA is the cell’s genetic material and contains the instructions for making proteins. The Eukaryotic Cell has a nucleus in its center whose DNA is enclosed by nuclear membranes. The nucleus contains most of the cell’s DNA.
- The Golgi bodies are small sacs that are found in the cell membrane and which contain protein synthesis machinery.
- The Lysosome is another organelle that is located in the cell cytoplasm. It consists of vesicles that are membranous sacs containing digestive enzymes. They are responsible for breaking down complex molecules into simple compounds.
- The Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles of eukaryotic cells. They have double membranes that contain enzymes and smaller organelles called mitochondria.
- The Nucleus is the control center of the cell. In eukaryotes, it contains many organelles that carry out the specialized functions of the cell. The Nucleus contains ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus also contains DNA, which is the chemical code for building proteins in cells.
- The Nucleolus is a ribosome-like organelle that contains RNA. The Nucleolus is involved in the synthesis of proteins, which help cells to function and divide. The Nucleolus also acts as a storage site for some of the genetic material in eukaryotic cells.
- The Ribosomes are large protein molecules that are the site of protein synthesis. They work in conjunction with messenger RNA, which is a small molecule that carries the information needed to produce proteins.
- The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) is an organelle that is found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It consists of membrane-bounded sacs or tubules that extend from the cell membrane to the nucleus. The tubules contain ribosomes, RNA, and other proteins.
- The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is an organelle that is found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It consists of tubules that extend from the cell membrane to the nucleus. The tubules are packed with proteins, lipids, and other organic material.
- The Vacuole in a plant cell is a membrane-bound organelle that helps regulate the cell’s water balance.
- The Vesicles are small vacuoles in the animal cell that are used for transporting materials within cells. They store a variety of molecules, including proteins and organelles.