Microscope is a biological instrument, mainly used in observing tiny things that cannot be seen by the naked eye. These very small things include cells, microorganisms, tiny animals and even small pieces of non-living materials. There are two types of microscope. These are the simple and the compound microscope. Simple microscope is composed of only one lens with low-powered magnification of 5 times. On the other hand, compound microscope is composed of two or more lenses which give high magnifying power.
Compound Light Microscope
Compound Light Microscope (CLM) is the most common type of microscope equipped with the combination of lenses. With this, compound light microscope can able to perform higher magnification. CLM has three main parts: mechanical parts, magnifying parts , and illuminating parts.
Mechanical Parts are what move the lens to allow the user to focus on different objects. There are usually three sets of mechanical parts: one for moving the lens up and down, one for moving it left and right, and one for rotating it around its vertical axis. These parts are typically controlled by a set of knobs or levers located on the side or front of the microscope.
a. base- is one of the most important parts of a microscope. It is a flat, circular piece of metal that screws onto the bottom of the microscope tube. The eyepiece rests on top of the base. The base also houses the objective lens and has a screw to hold it in place.

b. arm- serves as a handle when carrying the microscope from one place to another. The arm of a microscope is a metal rod that extends from the body of the microscope to the base. It is used to move the microscope up or down, left or right, and closer or further away from the object being viewed. The arm is also used to attach accessories such as cameras or slides.
c. body tube–is the long, cylindrical piece of glass or plastic that houses the optics. It is attached to the base and held in place by the eyepiece and objective lenses. The body tube also contains the light source, which is either an incandescent bulb or a fluorescent lamp. The light shines down onto the specimen, which is mounted on a slide, and passes through the optics to create an image.
d. revolving nosepiece-is a part that allows the user to quickly change between different objectives. The objectives are the lenses that are used to view the specimen. The revolving nosepiece holds the different objectives in place and allows them to be rotated into position. This makes it easy for the user to switch between different magnification levels. The revolving nosepiece also helps to keep the microscope stable, which ensures accurate images.
f. adjustment screws or knobs-are important parts because they help to focus the image. They also help to keep the microscope in place. The screws or knobs can be turned to change the focus of the image. They can also be turned to adjust the height of the microscope.
fine adjustment screw or knob-it is used to make very small adjustments to the focus of the microscope. This allows you to get a clear image of the specimen that you are viewing. The screw or knob can be turned either clockwise or counterclockwise to adjust the focus.
coarse adjustment screw or knob is used to bring the specimen into focus. It is a large, knurled knob located on the right side of the microscope, just below the eyepiece. The knob moves the stage up and down so that you can adjust how close or far away the specimen is from the lens.
h. stage- is the part of the instrument where the object to be examined is placed. It is a platform that can be raised or lowered and has an aperture in the center that allows light to pass through. The stage is also equipped with mechanical stages that allow it to be moved in all directions. This enables the user to position the object under the lens for examination.
i. stage clip- is a device that helps to secure the specimen in place on the microscope stage. The stage clip has two arms that open up and fit around the edges of the microscope stage. The arms are then squeezed together to hold the specimen in place. The stage clip can also be used to hold a slide in place while it is being examined under the microscope.
Illuminating Parts are the light that is used to see the specimen. The light can be either transmitted or reflected. The transmitted light shines through the specimen, and the reflected light bounces off of the specimen and is then seen by the eye. The type of light that is used depends on the type of microscope that is being used.
a. mirror- is an instrument that is used to direct light from a lamp into the eyepiece of a microscope. The mirror is mounted on a hinge so that it can be swung out of the way when not in use. The mirror is usually made from polished metal, and it has a curved surface that reflects light into the microscope.
b. diaphragm is an important part of the optical system. It helps to control the amount of light that enters the microscope. The diaphragm can be adjusted to allow more or less light to enter the microscope, depending on the brightness of the specimen and the desired level of contrast. The diaphragm also affects image sharpness and resolution.
Magnifying Parts are used to enlarging the image of an object that is being observed. The magnification can be increased by using different lenses on the microscope. There are three types of lenses that are commonly used on a microscope- the eyepiece
, the objective, and the condenser. The eyepiece is the lens that is closest to the observer’s eye and it has a magnification of 10x. The objective is the lens that is located in the barrel of the microscope and it has a magnification of either 2x, 4x, or 10x. The condenser is a lens that is used to focus light onto the specimen.
a. ocular lens- when looking at the microscopic world, there are a variety of different lenses that can be used to view objects. The most common lens is the ocular lens, which is found in most microscopes. This lens is responsible for gathering light and projecting it onto the object that is being viewed. It also helps to magnify the image so that it can be seen more clearly. The ocular lens is located in the eyepiece of the microscope, and it can be adjusted to help improve viewing conditions.
b. Objective lenses- are located in the three objectives:
A low power objective (LPO)- is an objective lens that can magnify specimen 10 times.
A high power objective (HPO)-is an objective lens that magnifies the specimen 40 times.
oil immersion objective (OIO)- it enlarges the specimen 100 times


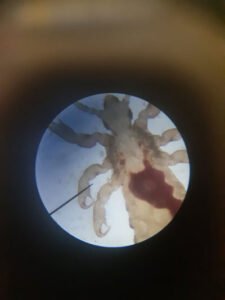
Question: What is the importance of microscope in medical field today?
Microscopy is the study of cells and tiny living things. It is also used in the field of medicine such as diagnosing diseases.